How To Test A Neon Transformer? Troubleshooting Steps And Voltage Checks
Testing a neon transformer is an essential skill for anyone who works with neon lighting. A faulty transformer can cause issues like flickering, dimming, or complete sign failure, but knowing how to test a neon transformer safely can help you avoid costly downtime and replacements.
In this guide, we walk you through visual inspections, input and output checks, and voltage readings with a multimeter. Whether you are an installer, sign owner, or repair technician, understanding the process of testing a neon sign transformer ensures reliable performance.
Key Takeaways
- Learning how to test a neon transformer helps ensure your neon signs remain safe, bright, and reliable.
- Never attempt to test neon sign transformer components without powering down and wearing proper personal protective equipment.
- After carrying out a visual inspection, you must test the input and output voltages and check against manufacturer specifications to verify that they are correct.
- We supply high-quality custom LED neon signs that don’t require transformers at all if you are looking for a simpler alternative.
How To Test A Neon Transformer?
When exploring how to test a neon transformer, preparation and safety cannot be overstated. It is important to start by disconnecting the sign from the power supply, ensuring no live current is present as you carry out your checks.
Before you connect any meters or tools, perform a visual inspection, looking for things like:
- Cracks
- Burnt areas
- Melted insulation
From here, disconnect the transformer to avoid false readings and use a multimeter to conduct an input test. Next comes the output test, measuring the transformer’s high-voltage terminals. More advanced users might test neon sign transformer performance under live load conditions to confirm real-time functionality, but this should only be done with extreme caution and protective gear.
Whether you are a custom neon sign maker, an electrician, or simply a neon sign user, understanding how to test neon sign transformer units with the following step-by-step method ensures accuracy and might extend sign lifespan.
|
Symptom |
Likely Cause |
Test to Perform |
Fix / Next Step |
|
Flickering tubes |
Low output voltage, failing electrodes, or poor connections |
Step 4: Output Test (multimeter across HV terminals) |
If voltage is low, replace transformer; if voltage is fine, inspect tubes/electrodes |
|
Buzzing or humming |
Internal coil breakdown, loose mounting, or moisture inside casing |
Step 2: Visual Inspection + Listen during Step 5 (Live Test) |
Tighten mounts, dry/replace transformer if moisture is present, replace if buzzing persists |
|
Sign won’t light at all |
No input power, blown fuse, or complete transformer failure |
Step 3: Input Test + Step 4: Output Test |
Restore mains supply or replace transformer if no output |
|
Dim or uneven glow |
Partial winding failure, poor electrode contact, or contamination in tubes |
Step 4: Output Test (compare to manufacturer spec) |
Replace transformer if voltage is below spec; otherwise, service/replace tubing |
Step 1: Safety First
Before learning how to test a neon transformer, you should understand that safety is paramount. Traditional neon signs use lots of electricity, and their transformers generate voltages ranging from 3,000 to over 15,000 volts - levels that can cause serious injury if mishandled.
Your first step should always be to disconnect power at the breaker. You should also wear protective gear like:
- Insulated gloves
- Protective eyewear
- Rubber-soled shoes
Make sure your work area is dry and free from conductive surfaces. When testing neon sign transformer components, treat all wires as though they are live until you verify otherwise. Skipping personal protective equipment is a common mistake that puts you at greater risk.
Safety also means using the right tools. You need a properly rated multimeter and insulated HV probes. Follow these precautions carefully to establish a foundation for safe troubleshooting.
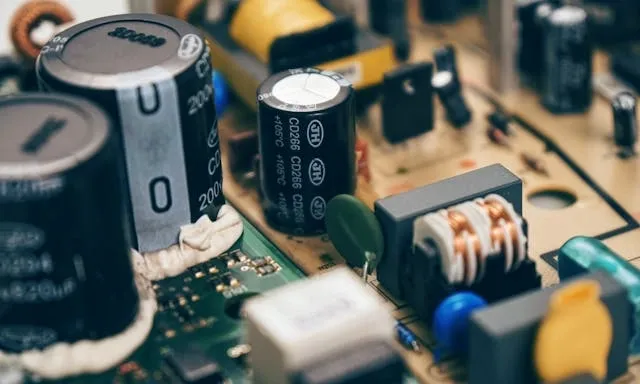
Step 2: Visual Inspection
Before you use instruments, carry out a careful visual inspection and you may quickly reveal the issue with your transformer. Clear signs of overheating or electrical failure include:
- Burn marks
- Melted insulation
- Cracked casings
Performance may also be affected by loose connections, frayed wires, or moisture buildup. When learning how to test neon sign transformer units, always note any unusual smells like burnt plastic, which can signal internal damage.
Check the surrounding components as well, since damage to nearby wiring could cause similar effects to transformer faults. Don’t reconnect the power at this stage - simply record your findings. Testing neon sign transformer performance without addressing visible defects could lead to misleading results. If you discover issues like corrosion or arcing around terminals, replacement is usually the safest option.
A thorough visual inspection might help you avoid unnecessary live testing. To avoid all of this entirely, purchase a simpler LED solution like a custom back-lit sign.
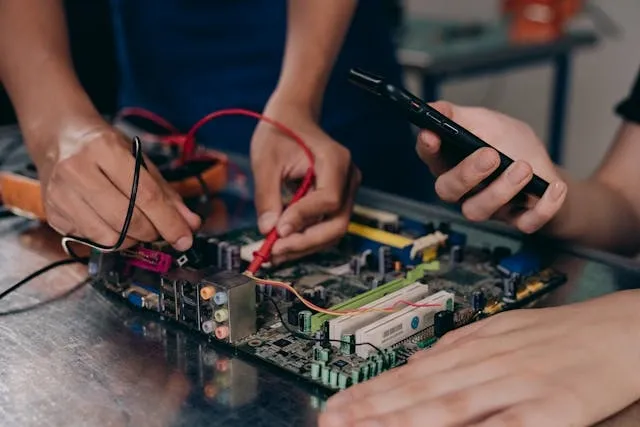
Step 3: Input Test
An input test will confirm whether your transformer is receiving the proper supply voltage. After turning off power, connect your multimeter leads to the input terminals. Restore power carefully and measure the voltage, ensuring it matches your local mains standard, which is:
- 120V in the U.S.
- 230V in Europe
Knowing how to test a neon transformer at this stage helps determine whether the issues come from the building’s electrical supply or the transformer itself. If your input voltage is absent or not stable, the problem is not with your transformer.
If the correct voltage is present but the sign fails, you will need to continue testing your neon sign transformer output. Always handle probes with care and stand clear of live parts. It’s important to carry out this step before moving on to high-voltage output checks.
As you deal with this high-voltage equipment, be mindful that modern research shows that energy-efficiency is important as it minimizes environmental impact, reduces energy bills, and improves national energy security. Consider a more modern alternative to traditional neon signs.
Step 4: Output Test
Once you have verified the input voltage, you can test the transformer’s high-voltage output. Switch off the power then connect a multimeter that is rated for high voltage to the transformer’s output terminals.
Carefully restore power and take the reading. Compare the measurement with the manufacturer’s specifications - typically between 3,000 and 15,000 volts. For instance, the P5G Style Servicemaster neon transformer has an output of 15,000 volts. If the output is significantly lower, it may indicate internal winding failure, while no output suggests a complete malfunction.
Testing neon sign transformer output safely requires high-quality equipment and protective gear as accidental contact could be extremely dangerous. If readings fall within range, but the sign still flickers or fails, the problem might be in the tubing or electrodes.
If you are finding electrical signage frustrating, you could opt for alternatives like custom vinyl banners and wooden signage. Working with our customers, we have found that strategic use of these non-electrical signage options can be just as effective as neon and LED signs.
Step 5: Live Voltage Test
A live voltage test is the final, most advanced diagnostic step for how to test a neon sign transformer. It allows you to measure voltage while the transformer is actively powering the sign. Be mindful that testing neon sign transformer output under load exposes you to extremely high voltages - LED signs use 20-60% less power for the same light output. For live testing, personal protective equipment is mandatory.
You will also need:
- Insulated probes
- A high-voltage multimeter
- Safety barriers
With the sign connected, measure across the transformer’s terminals and compare readings to manufacturer specifications. This confirms whether the transformer performs correctly under real-world conditions. If you observe flickering, buzzing, or voltage drops, these are signs of underlying issues.
Due to the risks, this process should only be carried out by experienced individuals. Live testing provides the clearest performance data, but it must be approached cautiously.
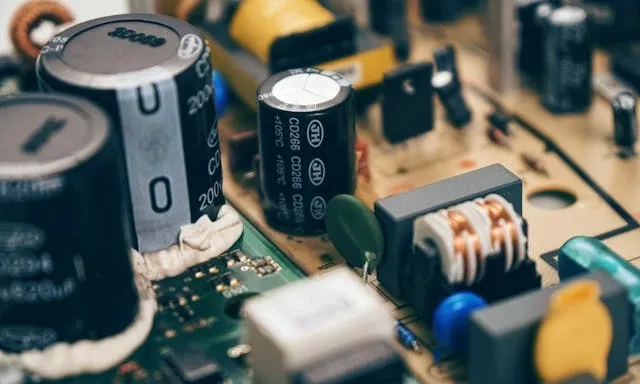
How To Check A Neon Sign Transformer?
To accurately check a neon sign transformer, it is essential to confirm both its input and output performance. Start by ensuring the power to this unit is properly supplied - in other words, verify the mains voltage at the input terminals with a multimeter.
If the input is stable, you must move on to measuring the output voltage. Knowing how to test neon sign transformer readings involves comparing the results from these tests with the manufacturer’s specifications - the output voltage should typically be between 3,000 and 15,000 volts.
The warning signs that there is an issue include:
- Overheating
- Buzzing sounds
- Flickering neon tubes
Always use insulated tools and follow safety protocols to the letter, as high-voltage output is dangerous. Interpret results accurately to determine whether replacement is necessary. If it is, consider LED neon vs glass neon lights and weigh the benefits of an entirely new product that runs on LED technology.
Tools Needed To Test A Neon Sign Transformer
It takes specialized tools to test a neon sign transformer unit safely. Anyone learning how to test a neon transformer must understand that incorrect tools can increase risks significantly. Let’s look at the tools you will need:
- High-voltage-rated digital multimeter: Your multimeter must be capable of handling the transformer’s significant output range.
- Insulated probes: These are important for protecting against accidental contact during testing.
- Professional equipment: For professionals, additional tools like clamp meters and protective barriers may be used.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): You should consider wearing gloves, safety glasses, and rubber-soled footwear to avoid unnecessary risk.
If your transformer fails testing, replacement may be the safest option. In such cases, consider upgrading to a modern alternative like our custom neon flex signs that achieve the same aesthetic using LED technology for superior durability, simpler performance, greater affordability, and much better energy efficiency.
Looking for a simpler neon sign alternative?
Work with us to create custom LED signs that don’t require transformers and operate at a lower voltage.
How Many Volts Does A Neon Transformer Put Out?
Neon sign transformers operate at very high voltages, typically ranging between 3,000 and 15,000 volts. Smaller signs may require a lower voltage, while larger installations with extended tube runs require a higher output.
When learning how to test neon sign transformer units, understanding expected voltage ranges is important to get accurate readings. As these high voltages pose serious safety concerns, extreme caution should be taken during every assessment. Only work with equipment rated for high-voltage applications, and observe proper safety practices.
If you attempt to test without preparation, you could experience things like:
- Dangerous electric shocks
- Equipment damage
Testing neon sign transformer performance with correct expectations ensures you know whether your unit is functioning normally or underperforming. Neon signs get hot, but should not become dangerously hot to the touch - test as soon as possible if you are concerned about your neon sign’s performance.
What Is The Output Voltage Of A Neon Sign Transformer?
The output voltage of a neon sign transformer is measured across high-voltage terminals and typically falls between 3,000 and 15,000 volts. When testing neon sign transformer performance, it is essential to compare your measurement with the manufacturer’s listed specification. Significant deviations indicate faults.
It is essential to use a high-voltage-rated multimeter as regular meters simply cannot safely handle this range. There are inherent risks with measuring live circuits, so full personal protective equipment (PPE) should always be worn. This includes:
- Insulated gloves
- Protective eyewear
- Non-conductive footwear
Understanding how to test a neon transformer under load also helps confirm its ability to power tubes effectively. Low readings could indicate worn internal coils, while no output indicates complete failure.
By carefully matching measured output to expected values, you can determine whether repair or replacement is the best course of action for your neon sign ideas.

Create unique neon signs for any purpose
With our service, you can make your own custom neon sign that works with LED technology - no transformers needed.
Learn moreDo Neon Signs Need A Transformer?
Traditional neon signs absolutely require a transformer to operate safely and effectively. Standard mains voltage (120V or 230V) is nowhere near enough to ionize the neon or argon gases inside the tubes.
The role of the transformer is to convert this low input into high voltage - usually between 3,000 and 15,000 volts. This is what is needed to initiate and sustain the glow. Attempting to run a neon sign without the correct transformer will result in failure to ignite, and it may even risk fire or electric shock.
Knowing how to test neon sign transformer units ensures your system is functioning properly, preventing unsafe conditions. Without a transformer, neon signage cannot function. This is not the same with custom LED signs, which have far simpler and lower-voltage specifications.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Test A Neon Transformer
How To Check A Neon Sign Transformer Easily?
The simplest way to check a neon sign transformer is to use a digital multimeter to measure both input and output voltage. Use proper tools and safety gear to ensure accurate results.
Do Neon Signs Need A Transformer Or Not?
Neon signs cannot function without a transformer. If testing neon sign transformer output reveals insufficient voltage, the sign won’t be able to sustain its glow.
Why Does My Neon Sign Work Sometimes And Not Others?
Many owners experience intermittent failures. These could be due to cycling issues, heat-related voltage drops, or failing GTO cable insulations.
